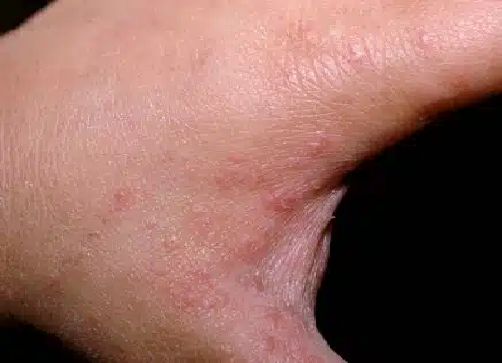
Scabies
Scabies is a skin condition caused by an infestation of the Sarcoptes scabiei mite. These tiny mites burrow into the skin, causing intense itching and a rash. It is highly contagious and typically spreads through close personal contact, such as skin-to-skin contact, or by sharing personal items like towels, clothing, or bedding. Scabies precautions and treatment is explained in detail below.
Symptoms of scabies
- Intense itching, especially at night
- Rash with small red bumps, blisters, or sores
- Sores or crusting from scratching
- Common areas affected include the wrists, elbows, armpits, genitals, and between the fingers
Diagnosis of Scabies
A healthcare provider can usually diagnose scabies by examining the rash and sometimes by taking a skin scraping to identify the mites.
Treatment of Scabies
- Prescription creams or lotions, such as permethrin or crotamiton, are the most common treatments.
- Oral medications, like ivermectin, may be prescribed for more severe or widespread infestations.
- Treating close contacts: Since scabies is highly contagious, anyone who has had close contact with an infected person should also be treated, even if they don’t show symptoms.
Scabies Precautions
- Avoiding close physical contact with someone who has scabies.
- Laundering clothes, bedding, and towels used by an infected person in hot water.
If you suspect you have scabies or are experiencing symptoms, it’s important to see a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment. So to get consultation Click here.