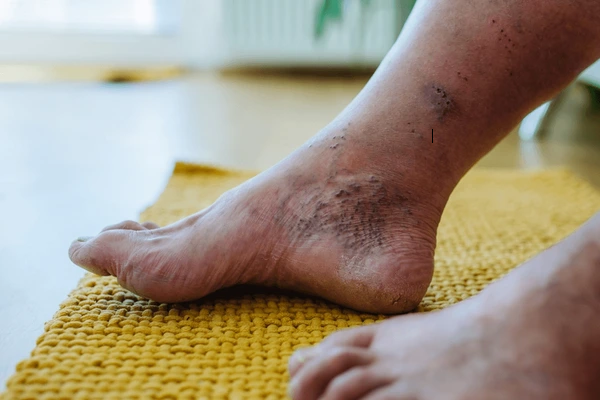
What is Diabetic Foot?
Diabetic foot refers to a range of foot problems that can occur in individuals with diabetes mellitus, stemming primarily from poor blood circulation and nerve damage (neuropathy) caused by prolonged high blood sugar levels. These conditions make the feet more prone to injury, infection, and, in severe cases, can lead to foot ulcers or even amputation if not managed properly. Diabetic foot management and causes are given below.
Key Risk Factors of diabetic foot
- Neuropathy: Nerve damage reduces sensation, so cuts or injuries may go unnoticed.
- Poor Circulation: Reduced blood flow impairs the body’s ability to heal, leading to slow healing of wounds.
- Infections: Diabetes weakens the immune system, making it easier for infections to develop and spread.
Common Diabetic Foot Problems
- Foot Ulcers: Open sores or wounds, usually on the bottom of the feet, which can become infected if not treated.
- Calluses and Corns: Increased pressure on certain areas can lead to callus formation, which can develop into ulcers.
- Fungal Infections: Fungal nail infections or athlete’s foot are common in diabetics and may spread quickly.
- Dry Skin and Cracks: Diabetic skin tends to be drier, making it more prone to cracking and infection.
Symptoms to Watch For
- Persistent pain, swelling, or redness
- Numbness or tingling in the feet
- Cuts or sores that do not heal
- Changes in skin color or temperature in the feet
- Unusual foot odor that doesn’t go away
Prevention and Care
- Daily Foot Checks: Inspect your feet for any cuts, blisters, or changes in color.
- Hygiene: Wash and thoroughly dry your feet daily, especially between the toes.
- Moisturize: Use lotion to prevent dryness but avoid the areas between toes to prevent fungal growth.
- Proper Footwear: Wear well-fitting, cushioned shoes to avoid pressure and reduce injury risk.
- Regular Medical Exams: See a healthcare provider regularly for foot assessments.
- Blood Sugar Control: Managing blood sugar levels helps minimize nerve damage and circulation issues.
Management of Diabetic Foot
If diabetic foot issues arise, treatment options can include antibiotics for infections, proper wound care, custom footwear, and sometimes surgical interventions for severe cases. It’s crucial for individuals with diabetes to stay proactive in foot care to prevent complications.